Pharmacy Automation: AI, Robotics & Future-Ready Pharmacy Solutions
introduction
Pharmacy automation integrates robotics, AI, and advanced software to streamline medication dispensing, inventory management, and patient safety. Modern automated pharmacy systems combine robotic arms, vision‐guided sensors, and self‑learning algorithms to handle high‑volume workflows with precision. Pharmacy AI powers predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and error recovery, while pharmacy robots perform simultaneous filling and picking at hundreds of items per hour. End‑to‑end pharmacy solutions extend to climate‐controlled storage, remote diagnostics, and 24/7 access kiosks. Leading providers like Ultravision—partnered with Label Elettronica—deliver turnkey implementations, backed by full consultancy, installation, and ongoing support. This article delves into definitions, architectures, implementation strategies, and the future of pharmacy automation.
What is Pharmacy Automation?
Pharmacy automation refers to the use of electronic, robotic, and software systems to automate tasks such as dispensing, sorting, packaging, and inventory management in pharmacies.
Early automation focused on pill counting, but has evolved to full robotic solutions that manage everything from product intake to order fulfilment.
Automated Pharmacy System: Architecture and Components
An automated pharmacy system is an integrated suite of hardware and software components—including modular shelving, robotic arms, vision systems, and management software—designed to automate the end‑to‑end medication workflow.
Key components include:
- Modular Shelving: Deep, reconfigurable racks tailored to millimetre precision for optimized storage density .
- Robotic Arms: Multi‑axis manipulators with pressure sensors (“Sense of Touch”) for secure handling of diverse package shapes and materials .
- Vision‑Guided Radar Sensors: Patent‑pending collision avoidance and pack‑realignment systems for uninterrupted operation .
- Management Software: AI‑driven control platforms that predict maintenance needs, optimize workflows, and provide intuitive touchscreen interfaces .
Pharmacy AI: Intelligence Powering Automation
Pharmacy AI encompasses machine‑learning algorithms and expert systems that drive decision‑making across the automated pharmacy.
- Predictive Diagnostics: AI models analyze sensor data to forecast equipment failures, enabling 98% remote resolution and rapid on‑site support .
- Demand Forecasting: Historical usage and seasonal trends inform inventory replenishment, reducing stockouts and overstock.
- Adaptive Shelf Layout: Self‑learning software reorganizes stock for fastest retrieval paths, minimizing robot travel time and improving throughput .
Pharmacy Robot: Precision Handling and Robotics
Pharmacy robots are at the heart of automation, capable of high‑speed, accurate manipulation of medication packs.
- High‑Speed Arms: Filling up to 800 packs/hour and picking up to 900 packs/hour, with optional dual‑arm configurations for parallel tasks .
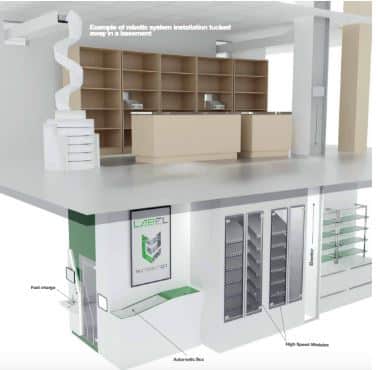
- High Speed Modules: Dedicated microchips enable each channel to dispense 10 products per second independently, maximizing throughput .
- Pressure‑Sensor Grippers: “Sense of Touch” technology ensures gentle yet secure handling of glass vials and irregularly shaped items .
- Radar Collision Prevention: Real‑time monitoring prevents pack misalignment and mechanical impacts, self‑correcting without human intervention .
Robotic dispensing systems significantly reduce miss‑picks and contamination risks by maintaining each drug in isolated cells and performing picture verification during retrieval.
Pharmacy Solutions: End-to-End Services for Pharmacies
Comprehensive pharmacy solutions encompass hardware, software, and service offerings tailored to each facility’s requirements.
- Automated Box: Hands‑off intake module that loads and scans incoming goods at 300 packs/hour with zero jamming .
- Medistore COOL & Cleaning Box: Climate control (ambient 25 °C or 2–8 °C chilled zones) plus scheduled sanitation of shelves during pharmacy downtime .
- Medistore 24 & Virtual Exhibitors: 24/7 digital kiosks for OTC access and interactive touchscreen displays showcasing product information and pricing .
- Management Dashboard: Intuitive, keyboard‑free software for real‑time system control via smartphone or tablet .
Pharmacy automation improves safety and operational efficiency: studies report reductions in medication errors, higher prescription volumes per pharmacist, and fewer manual tasks for staff.
Implementation Strategies for Pharmacy Automation
Successful deployment of an automated pharmacy system follows a phased approach:
- Site Assessment & Consultancy: 3D scanning and workflow analysis to model optimal layout and throughput .
- System Design & Integration: Customizing shelving dimensions, robotic arm placements, and software configurations to fit existing architecture .
- Installation & Validation: On‑site assembly of anodized‑aluminium modules through narrow access points, followed by IQ/OQ/PQ validation protocols .
- Staff Training & Change Management: Hands‑on workshops with Ultravision’s engineers to ensure smooth transition and adoption .
- Go‑Live & Continuous Optimization: Live monitoring during launch, with AI‑driven tuning and 24/7 support to refine processes and maximize ROI .
Benefits and Future Trends of Pharmacy Automation
Pharmacy automation delivers measurable gains:
- Efficiency: Up to 50% faster dispensing workflows and 30% reduction in labor costs.
- Safety: 70–90% fewer dispensing errors due to combined robotics and AI verification.
- Scalability: Modular design supports phased upgrades from basic counting to full robotic systems.
- Patient Satisfaction: Shorter wait times and improved service continuity, including remote and drive‑through options.
Emerging trends for 2025 and beyond include RFID inventory tracking, autonomous mobile delivery robots, and deeper AI integration for personalized medication management. The global market is projected to exceed $10 billion by 2030, driven by the need for error reduction and labor optimization.
Ultravision Automated Pharmacy and Other Services
Ultravision—partnered with Label Elettronica—provides turnkey automated pharmacy solutions plus a full suite of complementary services:
Medical Equipment Suppliers in UAE and Medical Equipment Suppliers in Dubai
As leading medical equipment suppliers in uae, Ultravision sources and integrates best‑in‑class robotics, compounding, and dispensing technologies.
Medical Equipment UAE: Ultrasound Machines & Healthcare Solutions
Ultravision also offers UAE expertise with high quality medical solutions, including high‑resolution ultrasound machines, comprehensive healthcare solutions, and digital imaging suites .
Medical Equipment Repair & Hospital Projects
We offer expert medical equipment repair and services, carried out by trained technicians to ensure maximum uptime and safe operation of your healthcare systems.

By combining advanced robotics, AI algorithms, and full‑service support, Ultravision’s automated pharmacy solutions set the standard for modern medication management, empowering pharmacies to achieve new levels of safety, efficiency, and patient care.
FAQ on Automated Pharmacy
What is pharmacy automation?
Pharmacy automation is the electronic process of distributing, sorting, packaging, and counting prescription medications using robotics and software to improve efficiency and accuracy.
How does an automated pharmacy system improve workflow?
By automating intake, storage optimization, and order picking, an automated pharmacy system reduces manual handling times by up to 50%, frees staff for clinical duties, and shortens patient wait times.
What role does pharmacy AI play in reducing dispensing errors?
Pharmacy AI applies machine‑learning algorithms to verify barcodes, predict mis‑picks, and self‑learn from exceptions—resulting in 70–90% fewer dispensing errors compared to manual workflows.
How reliable are pharmacy robot solutions in high‑volume settings?
High‑throughput pharmacy robots, like those filling 50,000 prescriptions/day in micro‑fulfillment centers, maintain >99.9% uptime thanks to collision‑prevention Radar systems and predictive diagnostics.
What pharmacy solutions are suitable for small independent pharmacies?
Compact modules—such as automated pill dispensers, small‑footprint vial fillers, and Adherence pouch packaging—allow independent pharmacies to automate key tasks without extensive infrastructure changes.
How can medical equipment suppliers in UAE integrate with pharmacy automation projects?
As leading medical equipment suppliers in uae, Ultravision provides end‑to‑end consultancy, 3D‑scanning site surveys, and turnkey installation of Label‑powered pharmacy robotics alongside other medical devices .
What services do medical equipment suppliers in Dubai offer for pharmacy robotics projects?
Medical equipment suppliers in dubai, like Ultravision, deliver system customization, on‑site final assembly, staff training, and 24/7 field‑engineer support for seamless pharmacy robotics deployments .
How do medical equipment UAE companies support ultrasound machines alongside pharmacy automation?
Ultravision bundles ultrasound machines and pharmacy solutions into integrated healthcare packages, ensuring both diagnostic and dispensing workflows are optimized under one service agreement .
What level of medical equipment repair is needed for automated pharmacy systems?
Automated systems require high‑skill medical equipment repair teams; Ultravision offers 98% remote troubleshooting and on‑site engineer dispatch within 3 hours to maintain >99% system availability .
How can healthcare solutions providers collaborate on hospital projects involving pharmacy and OR automation?
For large hospital projects, Ultravision’s integrated healthcare solutions team coordinates pharmacy robotics, modular OR design, and digital imaging suites—leveraging project management best practices to meet clinical, regulatory, and logistical requirements

